The international standards organization 3GPP, which is responsible for publishing technical specifications, has formulated 5.5G technical standards in 2021.
“The update named ‘Release 18’, which indicates the direction of 5.5G technology advancement, is expected to be completed by 3GPP in the first half of 2024,” said Song, chief marketing officer of Huawei Carrier Business Group.・Mr. Xiaodi said.
“This development shows that global suppliers are aligning their products to these standards, with 2024 expected to be the first year of commercial 5.5G deployment.”
The development of 5G technology is rapid and widespread. To date, more than 260 of his 5G networks have been deployed around the world, covering almost half of the world’s population.
In the 5.5G phase, Chinese companies aim to replicate this lead in construction speed.
China closes gap with South Korea and US in mobile memory chips
China closes gap with South Korea and US in mobile memory chips
The improvements that 5.5G brings are significant. Bandwidth for mobile users is expected to increase from 1 Gbps to 10 Gbps, latency will be significantly reduced, and advances in IoT technology through spectrum optimization and other technologies will provide high reliability and low latency for industrial production lines. will be used.
This evolution of technology is not only about science and engineering, but also about meeting the needs of users.
“In scientific advancement, it is often the scientists who break new ground and the engineers who make it happen. In telecommunications, engineers customize equipment based on the needs of users.” said Mr. Choi.

Traditional 5G focused on three things: bandwidth, latency, and number of connected users, but there was no need to optimize all three at the same time.
With 5.5G, dynamic spectrum allocation allows new base stations to actively distribute traffic, optimizing network resources for each user and significantly improving the user experience.
China’s leadership in 5G technology has already led to numerous industrial applications. 5.5G technology will further improve these applications.
China launches satellite internet that could challenge SpaceX’s Starlink
China launches satellite internet that could challenge SpaceX’s Starlink
High network quality gives operators a better sense of control and enables real-time response to field conditions.
Another notable example is the Qingdao Port in northern China, Asia’s first fully automated terminal, which has achieved world-class improvements in container loading and unloading efficiency thanks to millisecond-level data updates provided by 5G networks. We set a record.
As another example of industrial applications, China Telecom and fuel injection system supplier Nanyuedian Port (NYDK) are building 5G smart factories where robots connected to 5G signals accurately perform tasks such as feeding, processing, and transportation. I built it.
Efficiency has improved significantly, with the logistics robot now able to transport 1,800 parts in 90 round trips per day.
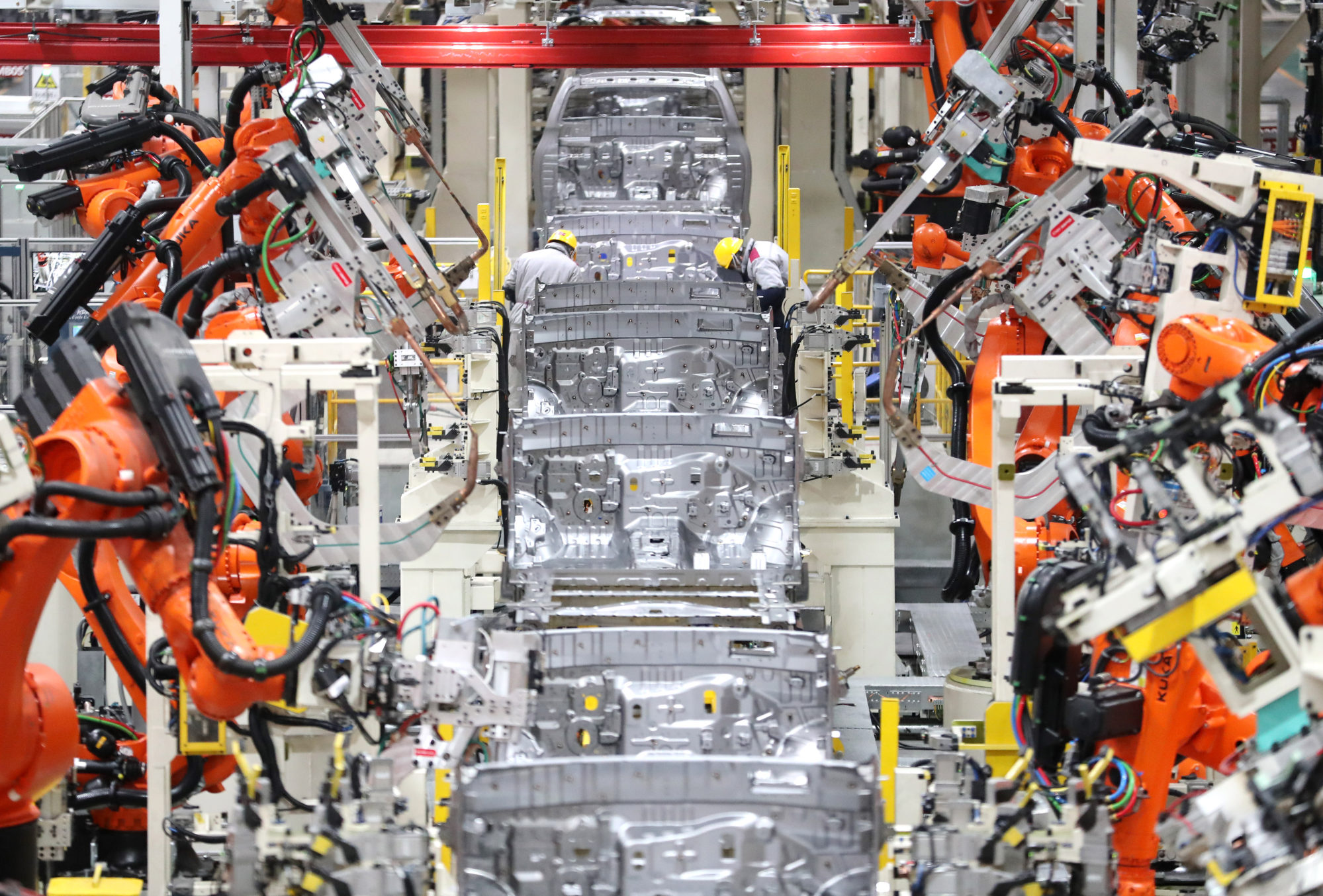
According to Song, the advancement of 5G-based IoT technology has also been driven by the introduction of 5.5G networks.
This will also be seen at the Hangzhou Asian Games in September 2023, where logistics vehicles in the Olympic Village will be powered by new lithium energy and use passive IoT technology enabled by 5.5G to ensure safety.
Previously, manual temperature checks and reporting were required to ensure battery safety, but with 5.5G, small vehicle-mounted tag modules can be used without power to base stations more than 200 meters (650 feet) away. Communicate with stations and achieve 99% accuracy. Increase in operational safety and efficiency.
However, the development and operating models for 5G technology are very different in China and the US, with US providers focusing more on high-value business users.
In the United States, “the cost of a single base station is much higher, reflecting a high-value operating model that provides precise business coverage,” according to an opinion piece posted on Huawei’s website.
US communications watchdog targets Chinese IoT parts maker
US communications watchdog targets Chinese IoT parts maker
This is in stark contrast to China’s approach. In the US, smart factory applications are not as common as they are in China.
Ericsson, a leading supplier of 5G devices, has established a smart factory in Lewisville, Texas, to assemble its 5G equipment. However, this kind of production line upgrade is not seen in other companies.
Ford Motor Co. is installing Ericsson 5G connectivity at its factories in Spain, but internet usage is not specified on its website. Inquiries from the Post Office to Ford and General Motors regarding the application of 5G in the companies’ manufacturing processes have not yet been answered.
This delay in industrial production during the 5G phase is likely to be further exacerbated in the 5.5G phase, especially for high-end core manufacturing processes that require rapid response, such as machining of auto parts.

The collaboration tested a prototype network on an automotive welding production line, recording the first application of 5G-A in an industrial control core link and the first technical validation of a fully wireless flexible production system.
Traditional industrial controls rely heavily on wired networks to operate equipment.
However, the movement and rotation of the robot arm in these setups can wear the cables and cause significant downtime. The introduction of 5.5G technology is expected to fundamentally solve this problem.
Reflecting the stage of development of mobile technology, Japan began commercial use of 4G in 2010, while China issued 4G licenses almost four years later in December 2013.
From railways to 5G: Why China is joining the Digital Silk Road
From railways to 5G: Why China is joining the Digital Silk Road
Following a similar pattern, South Korea announced commercial use of 5G in March 2019, followed by China a few months later.
“Currently, with 5.5G, China is not only catching up, but also at the forefront of application-level technology,” Wu Hequan, an academic at the Chinese Academy of Engineering and chairman of the China Internet Association, said in an interview with People’s Magazine. . every day.
At the Global MBB Forum 2023 held in Dubai in October, Huawei announced several 5.5G-based technology upgrades for carriers.
Song highlighted the introduction of RedCap technology, which stands for Reduced Capability, a simplified version of 5G, into the 5.5G module. This innovation will significantly reduce the complexity of existing 5G modules, leading to lower end module power consumption and cost.
RedCap maintains the unique benefits of 5G technology, such as low latency, precise positioning and slicing capabilities, all of which are inherited within RedCap.
For base stations, network coverage and capacity have been significantly increased and power consumption per bit has been reduced.
Yang Chaobin, Director of Huawei and President of ICT Products and Solutions, announced the indoor 5.5G solution at the conference.
Named LampSite Masu.
Chipmaker SMIC’s sales decline for third consecutive quarter despite Huawei’s boost
Chipmaker SMIC’s sales decline for third consecutive quarter despite Huawei’s boost
The device hibernates during idle time, consumes less than 1 watt of power, and quickly wakes up on demand, ensuring 24-hour energy efficiency.
While it is clear that 5.5G is widely applied in B2B contexts such as smart factories and mining, consumer applications are still sparse.
Mr. Choi pointed out that there is a lack of killer applications for 5.5G networks, and the per capita value conversion is not high.




