5G, the fifth generation of mobile phone technology, is not a single flavor. In fact, 5G is like a Naples that combines his three flavors with new advanced features that can be added to each type.
The different types of 5G consist of different frequencies on which 5G operates. low band, mid band and high band 5G. The difference between these flavors is that each It is said that they are related to different properties of the spectrum.
The individual characteristics of each 5G type are not inherently new. They aim to build on the capabilities of past generations and solve the problems they created. However, the different types of his 5G are noteworthy as they enable advanced applications and technologies that make his 5G unique for enterprise networks.
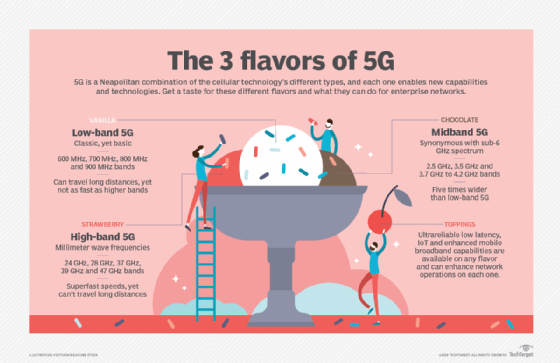
The different types of 5G can be compared to Neapolitan ice cream, a type of ice cream with three different flavors in one container. Low-band, mid-band, and high-band 5G are similar to vanilla, chocolate, and strawberry, respectively. The three major U.S. carriers (AT&T, T-Mobile, and Verizon) use all three frequency bands.
1. Low band 5G
Lowband is the closest 5G spectrum to 4G and 4G LTE, and operates on frequencies closest to TV and radio stations. That’s why it’s vanilla. It’s classic, everyone is familiar with it, and it’s pretty basic in terms of advanced frequencies.
 lindsay notwell
lindsay notwell
However, this doesn’t mean low-band 5G isn’t worth it. Notwell said low-band 5G is 10 times faster than 4G speeds, and this type of 5G can communicate over long distances. Some TV stations still use similar frequency bands because they can cover a wide area. According to the Federal Communications Commission (FCC), low-band 5G ranges from 600MHz to 900MHz.
However, low-band 5G isn’t as fast as the other flavors, which is why it can travel so far. Low-band 5G has less bandwidth. They have less ability to carry data than higher frequencies, so they can reach farther.
“This is kind of a double-edged sword,” Notwell said. “The bass has good range, frequency, and transparency properties, but it’s not very broad.”
2. Mid-band 5G
Mid-band 5G is like chocolate ice cream. It’s a little more advanced than the vanilla low band, but it’s not the most hyped of the various types of 5G. Midband is commonly synonymous with the sub-6 GHz spectrum, as it ranges from 2.5 GHz, 3.5 GHz, and 3.7 GHz to 4.2 GHz bands. Notwell said mid-band 5G spectrum is five times wider than low-band spectrum.
Mid-band 5G is wider than low-band 5G and has the capacity to transfer larger amounts of data, but it cannot communicate as far. Buildings and other solid objects can affect the higher range of mid-band 5G, but their penetration issues hinder high-band 5G more noticeably.
3. High band 5G and mmWave
High-band 5G is effectively the opposite of low-band 5G. It won’t be able to communicate over long distances, but it will have lightning-fast speeds resulting from 5G’s most touted benefits. High-band 5G correlates with strawberry ice cream as it adds a unique flavor of fast speeds to the Neapolitan combination. According to the FCC, high-band 5G includes the 24GHz, 28GHz, 37GHz, 39GHz, and 47GHz bands.
Just like strawberry ice cream contains tiny strawberries, high-band 5G contains even more surprising features. It’s millimeter wave (mmWave), a spectrum from 30 GHz to 300 GHz that provides faster connections and faster download speeds. These features, along with mmWave’s high bandwidth and ability to transmit more data between destinations, are driving global interest in 5G technology.
MmWave is also the only type of 5G that has potentially different use cases than other types. For example, data centers may require mmWave for failover because they are powered solely by fast, reliable fiber optics, Notwell said. MmWave supports the level of performance and speed that data centers require more than low-band or mid-band 5G. However, overall, use cases do not vary much by spectrum type.
One of the biggest challenges with high-band 5G for both carriers and enterprises is millimeter wave line-of-sight range, which limits the frequency’s reach. For example, heavy rain can also interfere with millimeter waves. Because of this limitation, Notwell said proper installation is critical to the success of his organization’s 5G deployment.
“If you were relying solely on millimeter waves, that would be a problem,” Notwell said. “But what we’re seeing is a new technology that allows 4G and 5G to operate on the same frequency. This is called dynamic spectrum sharing.”
Various other 5G features
Dynamic spectrum sharing is one of the features available in different types of 5G. This is like a variety of toppings available for all types of 5G technology. Other toppings and features include ultra-reliable low latency, IoT capabilities, and enhanced mobile broadband.
dynamic spectrum sharing
Thanks to dynamic spectrum sharing, different types of 5G frequencies can exist on the same spectrum as 4G. Notwell said this sharing will change with the demise of 2G and 3G, as carriers close spectrum allocated to 2G and 3G technologies and invest in spectrum where 4G and 5G can operate together. It is becoming more common.
Dynamic spectrum sharing benefits organizations that have already adopted 4G technology but aren’t sure if investing in 5G is worth it. 4G can still address many use cases. The strategy for many organizations is to “deploy with 4G and then connect 5G when and where you can,” Notwell said.
So, if an organization wants to add coffee ice cream to its 5G Neapolitan dessert, or 4G, dynamic spectrum sharing will enable that combination.
Extremely reliable and low latency
Each type of 5G technology supports highly reliable, low-latency connectivity, which enables rapid response to requests and provides benefits such as automation and video conferencing.
Additionally, this highly reliable, low-latency connection enables remote communication so companies don’t have to pay as much to fly employees to job fairs and conferences. , Notwell said, can save organizations money. With 5G, communication can happen instantaneously without the physical presence of a person. This connection also enhances facial recognition and video surveillance capabilities.
IoT function
Three different types of 5G enable large-scale machine-type communication. This is a feature that allows machines to communicate with each other without human intervention, similar to IoT. In particular, 5G enables narrowband IoT, a low-power IoT technology that can benefit and support a large number of his IoT devices.
Narrowband IoT also improves battery life in mobile devices, so IoT sensor batteries can last up to 10 years, Notwell said. Also, if your organization uses different systems for all your connected devices, 5G could reduce those systems to one network. With these new features, each type of HIS 5G aims to quickly and reliably support all connected devices on a single HIS 5G network.
Enhanced mobile broadband
This feature is exactly what it says. Enhanced Mobile Broadband improves the performance of standard mobile broadband. Mobile broadband enhancements can also reduce the cost of wired connectivity for organizations.
Enhanced mobile broadband offers faster, more flexible and more reliable connectivity than traditional cellular technology or Wi-Fi connections, leading experts to wonder if 5G will eradicate Wi-Fi. It’s all because of this enhanced broadband.
“You’re going to see wide area networking, the wired world, change dramatically to the wireless world because you have the freedom of location and time,” Notwell said. ”[A big] The problem retailers have is coordinating wiring installation and store opening dates. Well, wireless is already there, so just turn it on. ”
Editor’s note: This article has been updated to reflect changes in the use of 5G bands by carriers.


