What is 5G Standalone (5G SA)?
5G Standalone (5G SA) is cellular infrastructure purpose-built for 5G services by implementing 5G standards and protocols in the radio network and controller core. Also known as 5G standalone. Standalone 5Gor SA 5G.
Most carriers in the US and elsewhere are deploying 5G in a hybrid mode called . 5G non-standalone (5G NSA). With 5G NSA, carriers will use the new 5G radio equipment, but layer it on top of the existing 4G LTE core.
5G radio access networks (RANs) enable the use of 5G frequencies, allowing 5G-equipped endpoints to enjoy some of the promised benefits of 5G, primarily increased connection speeds and improved latency. . However, in hybrid networks, even with 5G endpoints, the full 5G feature set is not available and high-end 5G performance is still out of reach.
5G SA is an end-to-end true 5G network using 5G radios on the edge and 5G core. 5G standalone provides all the intended benefits of 5G without the limitations of 4G LTE. On the other hand, 5G NSA uses his 4G LTE core and cannot provide his 5G features other than wireless connectivity.
Why is 5G standalone important?
Faster downloads and faster links to online applications are great for individuals, but businesses want and need more from 5G. Businesses can use 5G to connect their sites more broadly and cost-effectively than 4G LTE services. Businesses also hope that 5G will provide a more reliable and flexible alternative to Wi-Fi. Wi-Fi use cases revolve around user devices such as laptops, phones, and tablets and Internet of Things (IoT) deployments.
Unlike 5G NSA, 5G standalone supports ultra-dense deployments, such as IoT use cases that include a high density of sensors and controllers within smart buildings. 5G SA can support up to 1 million devices within 1 square kilometer. It also supports ultra-low latency use cases that are not possible with 5G NSA, such as real-time control of robotic equipment in warehouses and factories.
Also of particular interest for enterprise site connectivity, 5G SA supports network slicing. This is a deployment mode that allows different devices and customers to obtain dedicated network partitions, such as virtual private cellular networks, with specified performance guarantees such as minimum and maximum throughput rates. 5G NSA cannot support slicing.
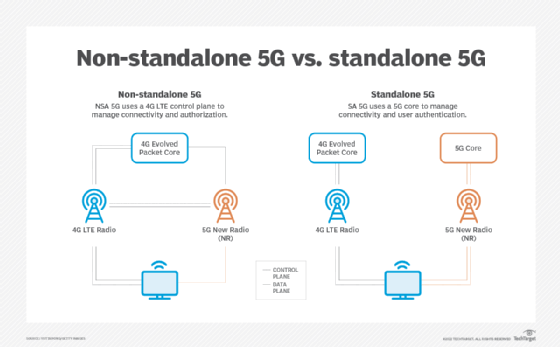
How does 5G standalone work?
5G SA will employ both a 5G-compliant RAN and a 5G-compliant core that combines traditional core and edge infrastructure.
5G devices such as phones, hotspots, cars, and fixed wireless modems establish connections to 5G access points (APs) through a new generation of antennas using radios in frequency ranges specified by the 5G standard. Masu. New antennas enable many improvements in signal reach, device throughput, and device density.
The APs communicate with edge and core 5G controllers that manage device connectivity and connectivity across the provider’s network. Within edge and core computing clusters, 5G standards rely on modern computing principles such as virtualization and microservices architectures consisting of containers and container orchestration platforms.
As a result, 5G network operators can move functions from edge to core to edge, easily and transparently scale up and down, and run core functions in both private and public cloud and edge infrastructure. Masu.
What are the benefits of 5G standalone?
With support for the full 5G feature set, businesses can realize the following benefits:
- 5G NSA brings even more speed and reach.
- Support for high-density deployment of devices.
- Support for low-latency and real-time use cases.
- Enhanced support for enterprise site connectivity through network slicing.
- Better security than 5G NSA.
- 5G SA supports only 5G and retains pre-4G standards, simplifying the RAN and core compared to 5G NSA. However, a 5G SA core alone is more complex than a pure 4G core alone.
Should businesses use 5G standalone?
Yes, businesses must use 5G SA. Without it, you won’t be able to reap the full benefits of 5G deployment.
5G non-standalone is not better than 4G LTE when it comes to supporting all potential enterprise use cases for cellular data services. 5G NSA has value as a bridge technology, allowing businesses to use their 5G-enabled equipment in a circular manner while carriers migrate their infrastructure, but this is only intended as a transition mode. The goal is 5G SA.
However, enterprise communications engineers should keep in mind that the 5G SA core is a new code stack that implements new protocols. On the other hand, it could mean leaving bugs and fixes in old systems, and the inevitable result is a 5G NSA-like patchwork with risks to functionality and security. On the other hand, new code is by definition less tried and tested, and as such can introduce surprising and dangerous bugs.


