Telecommunications industry players are already charting the course for next-generation mobile networks with an eye toward 6G. According to a recent report from Analysys Mason, organizations such as vendors, research institutes, academic institutions, carriers, and governments are actively working on envisioning and researching new 6G technologies.
According to a recent report from Analysys Mason, organizations such as vendors, research institutes, academic institutions, carriers, and governments are actively working on envisioning and researching new 6G technologies.
The report highlights that vendors are currently leading 6G research and development (R&D) projects, aiming to align future standards with evolving technology. But Analysis Mason urges carriers to emulate this proactive stance to ensure 6G technology translates into tangible commercial value.
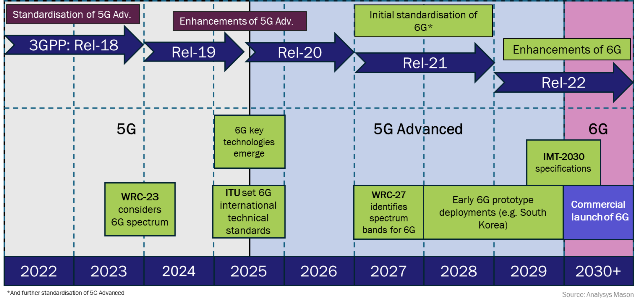
Although 5G networks are not yet widespread around the world, discussions about 6G are gaining momentum. According to the report, the next immediate step is the rollout of 5G Advanced, which is expected to technically optimize 5G networks by 2025.
Based on this foundation, 6G networks are expected to provide high-performance, AI-driven and sustainable connectivity, with standardization expected to begin around 2028. Following the finalization of the initial standard in 2028, the initial deployment of his 6G prototype will be followed by the full commercial launch of his 6G network from 2030.
The involvement of a variety of organizations, from vendors to governments, in 6G research and development highlights the global interest in shaping the future of telecommunications. Key technologies such as reconfigurable intelligent surfaces (RIS), photonic technology, and AI-enabled air interfaces (AI-AI) are already in early stage testing.
Despite widespread participation, the report notes disparities in operator involvement compared to vendors, research institutions, and academia. Analysys Mason analyst Stephen Burton emphasizes that carriers need to step up their 6G research and development efforts to ensure their technology is central to future standards and deployments.
Operator participation currently accounts for only 7% of all 6G R&D activity, but is primarily focused on key areas such as AI/ML integration, RAN hardening, and network security. By prioritizing these technologies, carriers aim to deliver resilient, secure, and cost-effective 6G networks that can support diverse applications across sectors.
Recognizing the potential pitfalls observed during the transition to 5G, carriers are being urged to take a more active role in shaping the trajectory of 6G development. This includes aligning research and development efforts with future market demands and revenue opportunities to ensure that investments in 6G technology yield strong returns.