5G is speeding things up, both figuratively and literally. If the latest predictions hold true, the future of 5G is bright. In 2020, Apple released the first iPhone to support 5G connectivity and operate on both mmWave and sub-6 GHz 5G. AT&T and Verizon both announced that their 5G service is available nationwide, and Verizon also announced that its 5G Ultra Wideband service (up to 4 Gbps) is available in some of its 71 cities. It was shown that T-Mobile, which acquired Sprint in April 2020, added 2,000 towns and cities to its 5G network with the launch of an independent architecture. This increased the total number of cities covered to more than 7,500.
But the more exciting aspect of 5G is that the collection of technologies known as 5G will become an integral part of the retail experience, fixed wireless access, manufacturing, healthcare, mobility, and the Internet of Things (IoT). It has not arrived yet. ).
But first consider your overall growth scope. The 2022 Ericsson Mobility Report predicts that 5G subscriptions will reach 4.4 billion worldwide by the end of 2027, accounting for approximately 48% of global mobile subscriptions. (It should be noted that while Ericsson, as a communications technology provider, has a vested interest in painting a rosy picture of 5G, the company’s oft-cited Mobility Report is highly regarded ) The report shows that 5G subscriber penetration will be much higher than that of 4G. Ericsson reported that in the second quarter of 2022 alone, his number of 5G subscribers with 5G-enabled devices increased by 70 million to reach approximately 690 million worldwide.
The number of 5G smartphones shipped in the United States is expected to reach 118.1 million by the end of 2022, up from 92.8 million in 2021, according to International Data Corp. (IDC). IDC predicts that by 2026, the number of 5G smartphones will reach 161.2 million.Ships within the United States
GSMA Intelligence predicts 5G growth will reach 2 billion 5G connections by 2025, led by Asia and the US.
Regardless of the numbers realized, growth comes at a significant cost. McKinsey & Company predicts that by 2030, only a quarter of the world’s population will have access to high-band 5G services, which will cost between $700 billion and $900 billion to deploy. This means that 5G coverage will be significantly expanded, but that expansion will cover much of the edge.
A February 2020 report from the McKinsey Global Institute said, “Connectivity providers will continue to face a tough road ahead given the scale of investments required, many of which have already made capital investments to strengthen their networks. “We are struggling to meet shareholder demand,” he said. World: Evolving connectivity beyond the 5G revolution. ”
How will retail benefit from 5G?
Retail is expected to be one of the biggest beneficiaries of 5G by the end of the decade. Particularly in densely populated areas where 5G coverage is expected to be widespread, 5G is expected to complement smart retail technologies such as shelf sensors, cashierless checkout, and QR codes.
In a November 2019 report, IHS Markit explained how 5G will contribute to the global economy. The report says brick-and-mortar retailers are looking to differentiate themselves with digital signage by combining it with ultra-high-definition (UHD) video, virtual reality, and augmented reality as a way to more effectively compete with online shopping. states that it may be possible to use 5G. . This will come in the form of expanded digital interactions with customers in-store.
Forrester Research says the benefits for retailers include “frictionless, end-to-end consumer experiences in the form of enhanced mobile broadband, massive machine-type communications (MTC), and ultra-reliable low latency.” It comes in the form of building blocks.” communication. ” MTC provides connectivity to a large number of devices that send small amounts of traffic intermittently. 5G mobile broadband will also facilitate virtual and remote support before, during and after the sale, including VR and AR services, smart screens and mobile cloud services, Forrester said.
Forrester said 5G communications will also increase transparency and efficiency in the retail supply chain as IoT sensors become more widespread. According to the GSMA, the North American IoT market is expected to reach 5.9 billion connections by 2025.
Demand for 5G manufacturing is increasing
According to McKinsey, leveraging analytics, artificial intelligence and advanced robotics in smart factories can have a significant impact on overall plant performance. The findings show that smart factories can improve operational efficiency at every stage of production, whether on a single assembly line or across multiple facilities. The industry is increasingly using low-latency private 5G networks to do this, analysts say.
As the industry considers 5G options, it can choose between building and controlling a private 5G network using its own spectrum or sourcing network slices from a provider’s public 5G wireless network. By 2030, more than 1,000 businesses and government agencies will have private 5G networks, according to Chris Antlitz, principal analyst at Technology Business Research. But in the short term, only the largest customers will use private networks, as overhauling factories to support 5G for automation could cost hundreds of millions of dollars. He said:
According to McKinsey, the GDP impact of connectivity in manufacturing could reach between $400 billion and $650 billion by the end of this decade.
5G will transform healthcare from head to toe
5G is sure to revolutionize every aspect of healthcare, from supply chain optimization to remote diagnostics and electronic medical record management. In its report on 5G in healthcare, PwC said large-scale deployment is not expected in many markets until 2025. (However, the company notes that the COVID-19 pandemic could accelerate this.) If a large-scale rollout does occur, PwC predicts that bed occupancy, We predict that 5G-compatible devices will be used to monitor the movement of doctors, nurses, and patients. and wearable medical devices.
The biggest changes will come through tactile communication and what has become known as the tactile internet. The International Telecommunication Union describes Haptic Internet as combining ultra-low latency with extremely high availability, reliability, and security. Tactile Internet allows doctors to treat patients remotely. PwC envisioned it as: “A surgeon’s movements at one facility will be instantly replicated by computerized equipment at another facility, something that surgeons specializing in complex surgeries may not be able to immediately respond to. This is an innovation that could be particularly beneficial to patients in rural and small areas.” ”
According to McKinsey, 5G-enabled healthcare could generate between $250 billion and $420 billion in global GDP by 2030.
Fixed wireless access attracts attention
Fixed wireless access (FWA) has been shunned by critics as fiber redundant, but 5G can be used to bring broadband internet service to homes that cannot or choose not to have wired service. We provide The main benefit is that it can deliver average speeds similar to fiber-based services at about a quarter of the cost, the GSMA said.
“For customers, the advent of 5G means previously unconnected households and communities will realize the benefits of higher speeds, higher capacity and bandwidth to support the growing number of IoT devices,” GSMA said. says in their November 2019 report, “The Internet of Things.” 5G era. ”
FWA has become one of the key use cases for 5G New Radio. 5G NR is a set of standards that will replace his 4G wireless communication standard for LTE networks. 5G NR supports fiber-like bandwidth transmission for applications such as streaming video and low-bandwidth transmission in large-scale (M2M) communications. 5G NR also handles vehicle-to-vehicle (V2V) and vehicle-to-infrastructure (V2I) transmissions with very low latency requirements.
FWA subscribers will need new customer premises equipment (CPE). According to Counterpoint Research, 5G CPE shipments for FWA are expected to exceed 1 billion units by 2030, with a CAGR of 47% over the next decade.
study of counterpoint We predict that FWA subscribers will grow from just 75 million in 2021 to 462 million by 2030.
5G in 2023 and beyond
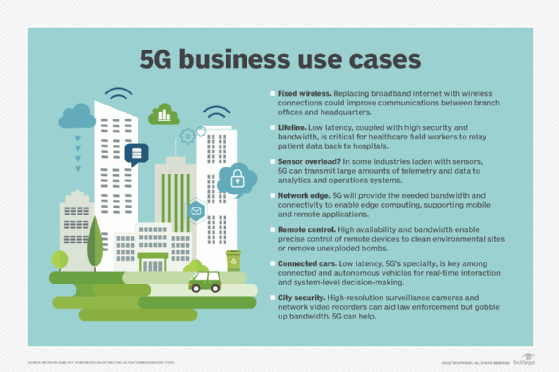
5G promises to bring the world to our mobile devices as we walk from point A to point B. But the real excitement is what 5G brings to intelligent mobility systems: car-sharing services, public transportation, V2I and V2V, shipping and receiving. . Add to this list smart cities that use 5G to improve operational efficiency, share information with citizens, and improve both the quality of government services and the welfare of residents. This includes improving traffic flow.
5G also holds great potential for businesses. Applications where 5G could have a significant impact include Citizen Broadband Radio Service (CBRS) and private networks. According to Research and Markets, the global 5G enterprise market is expected to reach $83.45 billion by 2031.
JPMorgan’s predictions for 5G are also very strong, with opportunities for companies contributing to accelerated growth. In North America alone, JP Morgan predicts that 5G will generate $180 billion in revenue by 2030.
“5G’s biggest opportunity lies with enterprises,” said Samik Chatterjee, senior communications and network equipment/IT hardware analyst at JPMorgan, in a report. “Companies are just beginning to scratch the surface in terms of investing in enterprise use cases.”
The overall impact that 5G will have around the world is overwhelming to understand. According to PwC, the total global impact of 5G by 2030 will reach $1.3 trillion.


